Velocity Control Mode
m_controller.setSetpoint(setPoint, ControlType.kVelocity);using namespace rev::spark;
m_controller.SetSetpoint(setPoint, SparkBase::ControlType::kVelocity);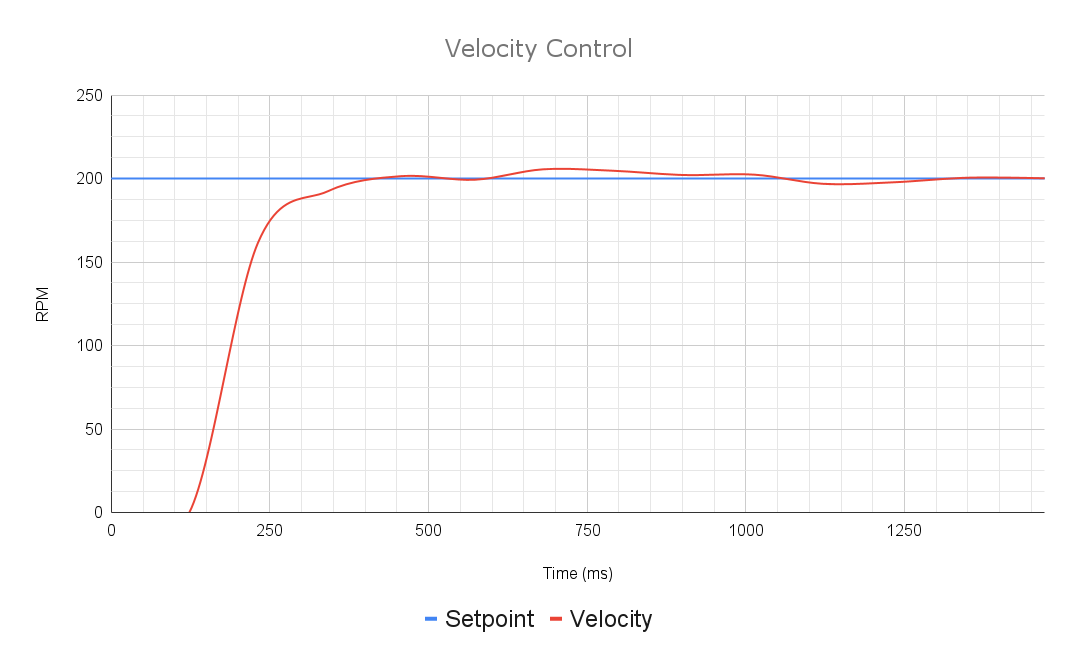
Last updated
Was this helpful?
m_controller.setSetpoint(setPoint, ControlType.kVelocity);using namespace rev::spark;
m_controller.SetSetpoint(setPoint, SparkBase::ControlType::kVelocity);
Last updated
Was this helpful?
Was this helpful?