Alternate Encoder Mode
The SPARK MAX can be configured to run in Alternate Encoder Mode, which reconfigures the Data Port on the top of the controller to accept an alternative quadrature encoder, separate from the default encoder inputs shared between the front Encoder Port and the default quadrature encoder Data Port pins. Analog input is not affected by Alternate Encoder Mode.
This feature is designed for use in low-RPM mechanisms such as drivetrains, arms, and other manipulators. For high RPM applications, it is recommended to use the built-in motor sensor for brushless motors or the default encoder inputs for brushed motors.
Alternate Encoder Specifications
Encoder Output Voltage Level
3.3V or 5.0V
Encoder Type Supported
Quadrature†
Maximum Counts per Second
165000
†
Index pulses are not currently supported
Before connecting a sensor with 5V output, the SPARK MAX must first be updated to firmware version 1.5.0 or later, or damage may occur. This can be done through the REV Hardware Client.
Maximum RPM with Common Quadrature Encoders
Encoder
Counts per Revolution
Max RPM
CTRE SRX Mag Encoder
4096
2400
Greyhill 63R256
1024
9600
When configured for Alternate Encoder Mode, a quadrature encoder connected to the reconfigured Data Port pins can be used as a feedback device by the SPARK MAX. Please note, the limit switch inputs cannot be used at the same time as an alternate encoder. The limit switch pins are repurposed for the alternate encoder and are thus disabled. Please see Connecting an Alternate Encoder for for more information.
Connecting an Alternate Encoder
Connecting an alternate encoder will likely require a custom wiring harness to connect the necessary encoder power, ground, and signals to the reconfigured Data Port. When configured in Alternate Encoder Mode, the Data Port has the following pinout:

Data Port Pinout in Alternate Encoder Mode
Connector Pin
Pin Type
Pin Function
1
Power
+3.3V
2
Power
+5V
3
Analog
Analog Input
4
Digital
Alternate Encoder Index†
5
Digital
Encoder B
6
Digital
Alternate Encoder A
7
Digital
Encoder A
8
Digital
Alternate Encoder B
9
Digital
Encoder C / Index
10
Ground
Ground
†
The Alternate Encoder Index pin is reserved but not currently supported
Use an Alternate Encoder Adapter (REV-11-1881) to connect a REV Through Bore Encoder directly to the SPARK MAX Data Port. This adapter has a JST PH 6-pin connector that is compatible with the Through Bore Encoder's pinout and a selection switch to change the signal that is connect to pin 4 of the data port.
Check out our documentation of the Through Bore Encoder.
Another option is the SPARK MAX Data Port Breakout Board. This board can be used to wire an alternate encoder to the Data Port. The following table describes which pads on the breakout should be used for which signals coming from the alternate encoder.
Alternate Encoder Pin-mapping for SPARK MAX Data Port Breakout Board
Breakout Board Pad Label
Alternate Encoder Function
Limit - F
Index†
P6 (P5 in older batches)
A
Limit - R
B
3.3V or 5.0V
Encoder Power
GND
Encoder Ground
†
The Alternate Encoder Index pin is reserved but not currently supported
Configuring and Using the Alternate Encoder Mode
Below you will find the steps required to set up and use the Alternate Encoder Mode on the SPARK MAX, starting with configuration through either the REV Hardware Client or the SPARK MAX APIs.
Configuration Using the REV Hardware Client
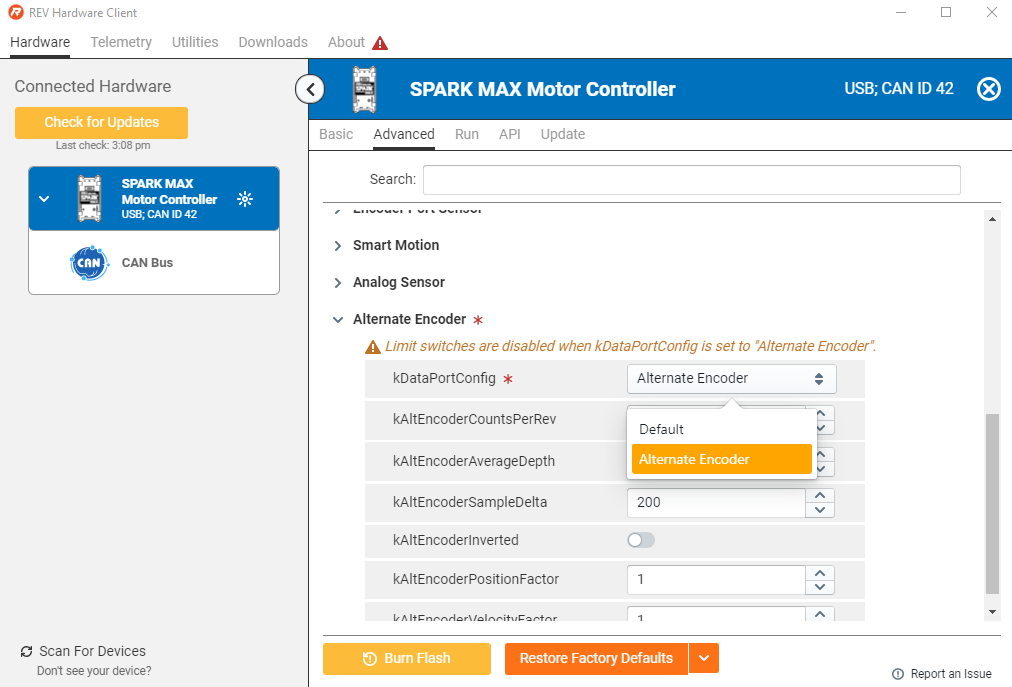
Using the REV Hardware Client, select your SPARK MAX, then navigate to the Advanced Tab and scroll to the Alternate Encoder parameter section. Enable the alternate encoder by setting the kDataPortConfig parameter to 'Alternate Encoder' via the drop down menu. You can also set the other Alternate Encoder parameters at this time.
Configuring Using the SPARK MAX APIs
If using the SPARK MAX APIs, the Alternate Encoder is automatically configured when the Alternate Encoder object is instantiated. An Alternate Encoder is created the same as a CANEncoder, either by directly using the constructor or calling GetAlternateEncoder() on a previously constructed CANSparkMax.
Currently, quadrature is the only available type of configuration for an alternate encoder. This is differentiated from the other types of encoder configurations available for an encoder connected through the front facing Encoder Port on the SPARK MAX.
Configuration Conflicts
Since the alternate encoder inputs and the default digital inputs are shared on the Data Port, the user cannot use both the alternate encoder and a digital inputs in code. Therefore, a std::invalid_argument (C++), IllegalArgumentException (Java), or an Error on the Error Out terminal (LabVIEW) will be thrown if a user tries to construct both types objects in code simultaneously.
Closed-Loop Control
The alternate encoder can be used with the different closed-loop control modes available on the SPARK MAX. The feedback device used by a CANPIDController must be set to use the alternate encoder through SetFeedbackDevice().
Initial Bring-up
Unlike the built-in sensor on the NEO Brushless motors, the 'phase' of the alternate encoder is unknown to the SPARK MAX. Before enabling any closed-loop control, it is critical that the phase is configured correctly. To verify:
Configure and connect the sensor as a quadrature alternate encoder, but do not run a closed-loop mode.
Plot the output signal of the motor using GetAppliedOutput() and the output of the encoder using altEncoder.GetVelocity(). Confirm that the sensor is behaving as expected. This can be done on the SmartDashboard:
frc::SmartDashboard::PutNumber("Alt Encoder Velocity", m_alternateEncoder.GetVelocity()); frc::SmartDashboard::PutNumber("Applied Output", m_motor.GetAppliedOutput());Verify that the sign of the sensor is correct relative to the motor direction when driving it forward and backward. If it is not, the sensor must be inverted by calling altEncoder.SetInverted(true).
Last updated
Was this helpful?

